It is important to clarify the difference between "traits" and "states". Personality tests focus on personality "traits," which are considered relatively stable characteristics, while "states" are temporary emotional or mental conditions. For example, extroversion is a trait, while feeling social is a state.
The words "tests" and "assessments" are often used interchangeably, but a test typically has questions that seek a correct answer, while an assessment is more often associated with questions that are correct only to the individual answering with no universal right or wrong answer.
Personality tests are often made up of numerous multiple-choice questions. A typical style of question might ask you to imagine yourself in a specific circumstance and then choose your response from a predetermined list that best describes how you react.
Some personality tests integrate images of a person or a setting and ask you to choose which one is most appealing.
History of Personality Tests
Personality tests have a long and varied history, dating back to ancient Greece, where philosophers such as Hippocrates and Aristotle made observations about the differences in human character and behavior.
One of the earliest attempts to uncover a person's character was by examining the bumps on their head. This process was called phrenology, and personality tests have come a long way since their inception. This practice is widely discredited and not considered a valid personality assessment method.
For centuries, people have been trying to assess others' personalities through different types of tests.
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, psychology emerged as a scientific discipline, and several theories about human personality were developed. The first systematic personality tests were created during this time, including the Woodworth Personal Data Sheet (1919) and the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (1940).
The latter part of the 20th century saw a proliferation of personality tests, with many new instruments being developed for both clinical and non-clinical purposes. These tests ranged from simple, self-administered questionnaires to complex, projective tests requiring trained administrators.
Personality testing was first taken seriously by the United States Army during World War I. Soldiers were tested in an attempt to determine who would be most likely to suffer the effects of shell shock based on their individual dispositions. There were ethical concerns surrounding this, and since then, personality testing has grown into being used by educational facilities and human resource departments worldwide.
Today, personality tests are widely used in a variety of settings, including clinical psychology, personnel selection and development, and market research. While there is still debate among psychologists about the validity and reliability of some personality tests, they continue to be popular and influential tools for understanding human personality and behavior.
Types of Personality Tests
There are numerous different personality tests that are used today. While they all use slightly different methods to classify respondents, they are all similar in test and question format.
Some of the most popular tests include:
The Enneagram Personality Test
The Enneagram test is a personality assessment. It is referred to as an assessment because there are no wrong answers. It divides all human personalities into nine types. Each type has similar characteristics to neighboring types, referred to as wings.
The Five-Factor Model
The CareerFitter
This career assessment test is primarily a hybrid personality test and career test that evaluates your personality, specifically in a work environment. CareerFitter uses the expression "work personality." They differentiate a person's personality when they are working and not working.This career assessment test asks the test taker questions about how they would respond to situations specific to a work setting. During the assessment, the test taker can see in real-time how their answers affect the results.The test has built-in superfluidity, so the examinee does not have to be concerned with an answer they were not 100% confident about.
Also, the answers are non-bias, meaning there are no wrong answers, and therefore, this career test should be considered more of an assessment or evaluation.The science behind CareerFitter was developed using psychological research and data that determines your work personality profile and, uncovers strengths and weaknesses, management styles, work environment preferences, and suggests careers and jobs that would best fit the examinee.
It's noteworthy that they’ve been around for over 25 years and are arguably one of the best career tests available, combining a work personality assessment with their aptitude aversion assessment— accessible exclusively to paid users.It is most often used by people looking to change careers that need career direction, college students, career coaches, and HR departments.
16 Personalities Test
-
Analysts
-
Diplomats
-
Sentinels
-
Explorers
Myers-Briggs Test
The original Myers-Briggs Test is considered by many to be one of the founding personality tests that rose to popularity in the 1900s. In 1917, Katharine Briggs became intrigued about personality types when her daughter chose an unlikely match for her fiance. She wanted to find out more about human characteristics and what caused people to have different personality traits.Both Katharine and her daughter worked together for the next 20 years. They relied heavily on Dr. Carl Jung’s research and together created the Myers-Briggs Personality Test.This test aims to determine how respondents see the world around them. It breaks personalities into four categories: introversion or extraversion, sensing or intuition, thinking or feeling, and judging or perceiving. A personality profile can be determined based on where each person falls within each category.
The Winslow Personality Profile
Process Communication Profile
NASA initially developed this test as a method to determine the underlying personality traits of its astronauts. They wanted to create a way to determine if the astronauts they had chosen were suitable for the job, how they would perform under stressful situations, what their preferred communication style was, and how well they would interact with other astronauts.This test divides respondents into six different personality categories.These are:
- Harmonizers
- Thinkers
- Rebels
- Imagineers
- Persisters
- Promoters
The Process Communication Profile test aims to show where a person's area of most significant strength is.
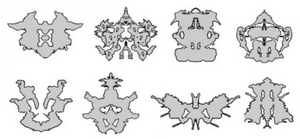
The Holtzman Inkblot Technique
DISC Assessment
William Marston and Walter Clarke first developed the DISC Assessment test. These psychologists designed a test to look into the strong behavioral traits of dominance, inducement, submission, and compliance.
This personality test can be very valuable to use in the workplace as it gauges how a person will react to specific rules, environments, and management styles. It can determine how well a potential candidate will fit into a particular role.
Advantages of Personality Tests
- They speed up the recruitment process - Allowing potential candidates to complete a personality test can give you a clear picture of who that candidate is without having to go through lengthy hiring and interviewing processes.
- They give you a deeper understanding of the candidate - A personality test can give you a better understanding of the likes, dislikes, strengths, and weaknesses of a candidate that you may not otherwise grasp from the normal interview process.
- They allow you to identify the "wrong" employees quickly - You are better able to weed out those with personality traits that don’t work with your corporate image or environment.
- They are cost-effective - Personality tests are relatively simple to complete and can save a company significant time and money compared to other interviewing techniques.
 Disadvantages of Personality Tests
Disadvantages of Personality Tests
While personality tests can be highly beneficial, they do come with their downfalls as well. Some of the most significant disadvantages to personality tests include:
-
Personality tests have the potential for social desirability bias. This refers to the tendency for individuals to respond to questions in a way that they think is most socially acceptable or desirable rather than accurately reflecting their true thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
-
Additionally, self-awareness is a key factor in the accuracy of personality tests. If an individual has limited self-awareness or lacks insight into their own thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, they may struggle to answer questions on a personality test accurately.
-
Some respondents may suffer from test anxiety. Test anxiety may cause an excellent respondent to finish with poor results due to their stress and anxiety levels while taking the test.
-
Some tests may not consider cultural differences, meaning people with different cultural backgrounds may not be able to answer specific questions, or their belief systems and traditions may not be accurately represented.
-
It is important to note that no test can capture the entirety of an individual's personality, and results are influenced by a variety of factors, including the individual's current state, the context in which the test is taken, and the questions being asked. As such, it is important to interpret the results of personality tests with needed confirmation and consider them to be part of a broader understanding of an individual's personality.







