Dental Hygienist
Does this career fit your work personality?
Begin The Career Assessment Test- Best Fitting Careers
- Work Personality Strengths
- Work Style Preferences
- and more
Job Outlook
Employment of dental hygienists is projected to grow 7 percent from 2022 to 2032, faster than the average for all occupations.
About 16,400 openings for dental hygienists are projected each year, on average, over the decade. Many of those openings are expected to result from the need to replace workers who transfer to different occupations or exit the labor force, such as to retire.
Education Details
Summary of What they do:
Administer oral hygiene care to patients. Assess patient oral hygiene problems or needs and maintain health records. Advise patients on oral health maintenance and disease prevention. May provide advanced care such as providing fluoride treatment or administering topical anesthesia.
What Dental Hygienists Do
Dental hygienists examine patients for signs of oral diseases, such as gingivitis, and provide preventive care, including oral hygiene. They also educate patients about oral health.
Duties
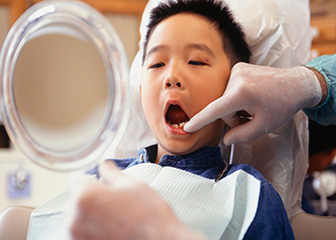
Dental hygienists typically do the following:
- Remove tartar, stains, and plaque from teeth
- Apply sealants and fluorides to help protect teeth
- Take and develop dental x rays
- Assess patients’ oral health and report findings to dentists
- Document patient care and treatment plans
- Educate patients about oral hygiene techniques, such as how to brush and floss correctly
Dental hygienists use many types of tools—including hand, power, and ultrasonic tools—in their work. In some cases, they use lasers. Hygienists remove stains with an air-polishing device, which sprays a combination of air, water, and baking soda. They polish teeth with a power tool that works like an automatic toothbrush. Hygienists also use x-ray machines to take pictures to check for tooth or jaw problems.
Dental hygienists talk to patients about ways to keep their teeth and gums healthy. For example, they may explain the relationship between diet and oral health. They may also advise patients on how to select toothbrushes and other oral care devices.
The tasks hygienists may perform, and the extent to which they must be supervised by a dentist, vary by state and by the setting in which the dental hygienist works. A few states allow hygienists with additional training, sometimes called dental therapists, to provide some restorative services, such as extracting primary teeth and placing temporary crowns.
Important Qualities
Critical thinking. Dental hygienists must be able to assess and evaluate patients and to develop oral hygiene care plans.
Communication skills. Dental hygienists must share information with dentists and patients about oral health status, oral hygiene care plans, and, if necessary, lifestyle counseling.
Detail oriented. Dental hygienists must follow specific rules and protocols to help dentists diagnose and treat a patient. Depending on the state in which they work and/or the treatment provided, dental hygienists may work without the direct supervision of a dentist.
Dexterity. Dental hygienists must be good at working with their hands. They generally work in tight spaces on a small part of the body, which requires fine motor skills using precise tools and instruments.
Interpersonal skills. Dental hygienists work closely with dentists. They also must be considerate in working with patients, especially with those who are sensitive to pain or who have fears about undergoing dental treatment.
Problem-solving skills. Dental hygienists develop and implement oral hygiene care plans to maintain or improve patients’ oral health.
Tasks On The Job
- Administer local anesthetic agents.
- Apply fluorides or other cavity preventing agents to arrest dental decay.
- Attend continuing education courses to maintain or update skills.
- Chart conditions of decay and disease for diagnosis and treatment by dentist.
- Clean calcareous deposits, accretions, and stains from teeth and beneath margins of gums, using dental instruments.
- Conduct dental health clinics for community groups to augment services of dentist.
- Examine gums, using probes, to locate periodontal recessed gums and signs of gum disease.
- Expose and develop x-ray film.
- Feel and visually examine gums for sores and signs of disease.
- Feel lymph nodes under patient's chin to detect swelling or tenderness that could indicate presence of oral cancer.
- Maintain dental equipment and sharpen and sterilize dental instruments.
- Maintain patient recall system.
- Make impressions for study casts.
- Provide clinical services or health education to improve and maintain the oral health of patients or the general public.
- Record and review patient medical histories.
- Remove excess cement from coronal surfaces of teeth.

PERSONALITY

| Your Assessment Results |
CAREER CHARACTERISTICS
Importance
|
|---|
|
?
? ? ?
|
97% | Concern for Others - Job requires being sensitive to others' needs and feelings and being understanding and helpful on the job. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
96% | Integrity - Job requires being honest and ethical. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
94% | Dependability - Job requires being reliable, responsible, and dependable, and fulfilling obligations. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
93% | Cooperation - Job requires being pleasant with others on the job and displaying a good-natured, cooperative attitude. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
91% | Self-Control - Job requires maintaining composure, keeping emotions in check, controlling anger, and avoiding aggressive behavior, even in very difficult situations. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
87% | Adaptability/Flexibility - Job requires being open to change (positive or negative) and to considerable variety in the workplace. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
87% | Attention to Detail - Job requires being careful about detail and thorough in completing work tasks. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
87% | Independence - Job requires developing one's own ways of doing things, guiding oneself with little or no supervision, and depending on oneself to get things done. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
86% | Stress Tolerance - Job requires accepting criticism and dealing calmly and effectively with high-stress situations. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
81% | Social Orientation - Job requires preferring to work with others rather than alone, and being personally connected with others on the job. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
76% | Initiative - Job requires a willingness to take on responsibilities and challenges. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
73% | Achievement/Effort - Job requires establishing and maintaining personally challenging achievement goals and exerting effort toward mastering tasks. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
72% | Persistence - Job requires persistence in the face of obstacles. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
60% | Analytical Thinking - Job requires analyzing information and using logic to address work-related issues and problems. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
57% | Leadership - Job requires a willingness to lead, take charge, and offer opinions and direction. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
55% | Innovation - Job requires creativity and alternative thinking to develop new ideas for and answers to work-related problems. | |
| Your Assessment Results |
IMPORTANT STRENGTHS
Importance
|
|---|
|
?
? ? ?
|
74% | Social - Work involves helping, teaching, advising, assisting, or providing service to others. Social occupations are often associated with social, health care, personal service, teaching/education, or religious activities. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
69% | Realistic - Work involves designing, building, or repairing of equipment, materials, or structures, engaging in physical activity, or working outdoors. Realistic occupations are often associated with engineering, mechanics and electronics, construction, woodworking, transportation, machine operation, agriculture, animal services, physical or manual labor, athletics, or protective services. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
61% | Investigative - Work involves studying and researching non-living objects, living organisms, disease or other forms of impairment, or human behavior. Investigative occupations are often associated with physical, life, medical, or social sciences, and can be found in the fields of humanities, mathematics/statistics, information technology, or health care service. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
55% | Conventional - Work involves following procedures and regulations to organize information or data, typically in a business setting. Conventional occupations are often associated with office work, accounting, mathematics/statistics, information technology, finance, or human resources. | |
| Your Assessment Results |
WORK VALUES
Importance
|
|---|
|
?
? ? ?
|
95% | Relationships - Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to provide service to others and work with co-workers in a friendly non-competitive environment. Corresponding needs are Co-workers, Moral Values and Social Service. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
67% | Support - Occupations that satisfy this work value offer supportive management that stands behind employees. Corresponding needs are Company Policies, Supervision: Human Relations and Supervision: Technical. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
61% | Independence - Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to work on their own and make decisions. Corresponding needs are Creativity, Responsibility and Autonomy. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
58% | Working Conditions - Occupations that satisfy this work value offer job security and good working conditions. Corresponding needs are Activity, Compensation, Independence, Security, Variety and Working Conditions. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
56% | Achievement - Occupations that satisfy this work value are results oriented and allow employees to use their strongest abilities, giving them a feeling of accomplishment. Corresponding needs are Ability Utilization and Achievement. | |
APTITUDES

| Your Assessment Results |
ABILITIES | SKILLS
Importance
|
|---|
|
?
? ? ?
|
72% | Problem Sensitivity - The ability to tell when something is wrong or is likely to go wrong. It does not involve solving the problem, only recognizing that there is a problem. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
72% | Arm-Hand Steadiness - The ability to keep your hand and arm steady while moving your arm or while holding your arm and hand in one position. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
72% | Finger Dexterity - The ability to make precisely coordinated movements of the fingers of one or both hands to grasp, manipulate, or assemble very small objects. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
72% | Near Vision - The ability to see details at close range (within a few feet of the observer). | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
69% | Oral Comprehension - The ability to listen to and understand information and ideas presented through spoken words and sentences. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
69% | Oral Expression - The ability to communicate information and ideas in speaking so others will understand. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
57% | Active Listening - Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
56% | Manual Dexterity - The ability to quickly move your hand, your hand together with your arm, or your two hands to grasp, manipulate, or assemble objects. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
56% | Speech Recognition - The ability to identify and understand the speech of another person. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
56% | Speech Clarity - The ability to speak clearly so others can understand you. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
53% | Written Comprehension - The ability to read and understand information and ideas presented in writing. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
53% | Inductive Reasoning - The ability to combine pieces of information to form general rules or conclusions (includes finding a relationship among seemingly unrelated events). | |
| Your Assessment Results |
TASKS | ACTIVITIES
Importance
|
|---|
|
?
? ? ?
|
90% | Establishing and Maintaining Interpersonal Relationships - Developing constructive and cooperative working relationships with others, and maintaining them over time. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
87% | Assisting and Caring for Others - Providing personal assistance, medical attention, emotional support, or other personal care to others such as coworkers, customers, or patients. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
82% | Performing for or Working Directly with the Public - Performing for people or dealing directly with the public. This includes serving customers in restaurants and stores, and receiving clients or guests. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
79% | Documenting/Recording Information - Entering, transcribing, recording, storing, or maintaining information in written or electronic/magnetic form. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
76% | Making Decisions and Solving Problems - Analyzing information and evaluating results to choose the best solution and solve problems. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
76% | Updating and Using Relevant Knowledge - Keeping up-to-date technically and applying new knowledge to your job. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
75% | Interpreting the Meaning of Information for Others - Translating or explaining what information means and how it can be used. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
74% | Handling and Moving Objects - Using hands and arms in handling, installing, positioning, and moving materials, and manipulating things. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
74% | Communicating with Supervisors, Peers, or Subordinates - Providing information to supervisors, co-workers, and subordinates by telephone, in written form, e-mail, or in person. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
72% | Getting Information - Observing, receiving, and otherwise obtaining information from all relevant sources. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
72% | Judging the Qualities of Objects, Services, or People - Assessing the value, importance, or quality of things or people. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
71% | Evaluating Information to Determine Compliance with Standards - Using relevant information and individual judgment to determine whether events or processes comply with laws, regulations, or standards. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
71% | Working with Computers - Using computers and computer systems (including hardware and software) to program, write software, set up functions, enter data, or process information. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
69% | Inspecting Equipment, Structures, or Materials - Inspecting equipment, structures, or materials to identify the cause of errors or other problems or defects. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
68% | Resolving Conflicts and Negotiating with Others - Handling complaints, settling disputes, and resolving grievances and conflicts, or otherwise negotiating with others. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
67% | Monitoring Processes, Materials, or Surroundings - Monitoring and reviewing information from materials, events, or the environment, to detect or assess problems. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
67% | Identifying Objects, Actions, and Events - Identifying information by categorizing, estimating, recognizing differences or similarities, and detecting changes in circumstances or events. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
66% | Selling or Influencing Others - Convincing others to buy merchandise/goods or to otherwise change their minds or actions. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
65% | Organizing, Planning, and Prioritizing Work - Developing specific goals and plans to prioritize, organize, and accomplish your work. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
64% | Communicating with People Outside the Organization - Communicating with people outside the organization, representing the organization to customers, the public, government, and other external sources. This information can be exchanged in person, in writing, or by telephone or e-mail. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
63% | Developing Objectives and Strategies - Establishing long-range objectives and specifying the strategies and actions to achieve them. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
62% | Performing General Physical Activities - Performing general physical activities includes doing activities that require considerable use of your arms and legs and moving your whole body, such as climbing, lifting, balancing, walking, stooping, and handling materials. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
62% | Processing Information - Compiling, coding, categorizing, calculating, tabulating, auditing, or verifying information or data. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
61% | Estimating the Quantifiable Characteristics of Products, Events, or Information - Estimating sizes, distances, and quantities; or determining time, costs, resources, or materials needed to perform a work activity. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
60% | Analyzing Data or Information - Identifying the underlying principles, reasons, or facts of information by breaking down information or data into separate parts. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
59% | Providing Consultation and Advice to Others - Providing guidance and expert advice to management or other groups on technical, systems-, or process-related topics. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
59% | Thinking Creatively - Developing, designing, or creating new applications, ideas, relationships, systems, or products, including artistic contributions. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
59% | Scheduling Work and Activities - Scheduling events, programs, and activities, as well as the work of others. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
59% | Coordinating the Work and Activities of Others - Getting members of a group to work together to accomplish tasks. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
54% | Training and Teaching Others - Identifying the educational needs of others, developing formal educational or training programs or classes, and teaching or instructing others. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
54% | Developing and Building Teams - Encouraging and building mutual trust, respect, and cooperation among team members. | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
51% | Coaching and Developing Others - Identifying the developmental needs of others and coaching, mentoring, or otherwise helping others to improve their knowledge or skills. | |
| Your Assessment Results |
CONTEXT | ATTRIBUTES
Importance
|
|---|
|
?
? ? ?
|
100% | Wear Common Protective or Safety Equipment such as Safety Shoes, Glasses, Gloves, Hearing Protection, Hard Hats, or Life Jackets - How often does this job require wearing common protective or safety equipment such as safety shoes, glasses, gloves, hearing protection, hard hats or life-jackets? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
100% | Indoors, Environmentally Controlled - How often does this job require working indoors in an environmentally controlled environment (like a warehouse with air conditioning)? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
100% | Spend Time Making Repetitive Motions - How much does this job require making repetitive motions? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
100% | Spend Time Using Your Hands to Handle, Control, or Feel Objects, Tools, or Controls - How much does this job require using your hands to handle, control, or feel objects, tools or controls? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
99% | Face-to-Face Discussions with Individuals and Within Teams - How frequently does your job require face-to-face discussions with individuals and within teams? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
99% | Contact With Others - How much does this job require the worker to be in contact with others (face-to-face, by telephone, or otherwise) in order to perform it? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
99% | Exposed to Disease or Infections - How often does this job require exposure to disease/infections? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
89% | Physical Proximity - To what extent does this job require the worker to perform job tasks physically close to other people? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
85% | Importance of Being Exact or Accurate - How important is being very exact or highly accurate in performing this job? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
84% | Frequency of Decision Making - How often is the worker required to make decisions that affect other people, the financial resources, and/or the image and reputation of the organization? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
83% | Impact of Decisions on Co-workers or Company Results - What results do your decisions usually have on other people or the image or reputation or financial resources of your employer? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
83% | Importance of Repeating Same Tasks - How important are continuous, repetitive, physical activities (like key entry) or mental activities (like checking entries in a ledger) to performing this job? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
78% | Determine Tasks, Priorities and Goals - How much freedom does the worker have in determining the tasks, priorities, or goals of the job? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
77% | Exposed to Radiation - How often does this job require exposure to radiation? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
77% | Spend Time Sitting - How much does this job require sitting? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
75% | Spend Time Bending or Twisting Your Body - How much does this job require bending or twisting your body? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
75% | Freedom to Make Decisions - How much decision making freedom, without supervision, does the job offer? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
74% | Work With or Contribute to a Work Group or Team - How important is it to work with or contribute to a work group or team in this job? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
72% | Deal With External Customers or the Public in General - How important is it to deal with external customers (as in retail sales) or the public in general (as in police work) in this job? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
69% | Time Pressure - How often does this job require the worker to meet strict deadlines? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
60% | Telephone Conversations - How often do you have telephone conversations in this job? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
59% | Consequence of Error - How serious would the result usually be if the worker made a mistake that was not easily correctable? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
56% | Dealing With Unpleasant, Angry, or Discourteous People - How frequently does the worker have to deal with unpleasant, angry, or discourteous individuals as part of the job requirements? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
54% | Exposed to Contaminants - How often does this job require working exposed to contaminants (such as pollutants, gases, dust or odors)? | |
|
?
? ? ?
|
53% | Health and Safety of Other Workers - How much responsibility is there for the health and safety of others in this job? | |
Work Environment
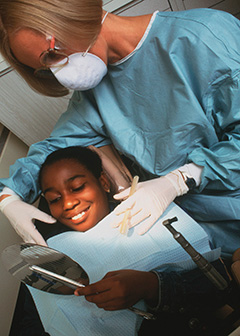
Dental hygienists held about 219,400 jobs in 2022. The largest employers of dental hygienists were as follows:
| Offices of dentists | 93% |
| Offices of physicians | 1 |
| Government | 1 |
Dental hygienists wear safety glasses, surgical masks, and gloves to protect themselves and patients from infectious diseases. When taking x rays, they follow procedures to protect themselves and patients from radiation.
Work Schedules
Many dental hygienists work part time. Dentists may hire hygienists to work only a few days a week, so some hygienists work for more than one dentist.
Getting Started
How to Become a Dental Hygienist
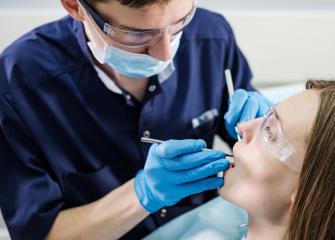
Dental hygienists typically need an associate’s degree in dental hygiene. Programs usually take 3 years to complete. All states require dental hygienists to be licensed; requirements vary by state.
Education
Dental hygienists typically need an associate’s degree in dental hygiene; they may also get a bachelor’s degree. Master’s degree programs in dental hygiene are available but are relatively uncommon. A bachelor’s or master’s degree usually is required for research, teaching, or clinical practice in public or school health programs.
Dental hygiene programs are often found in community colleges, technical schools, and universities. The Commission on Dental Accreditation, part of the American Dental Association, accredits more than 300 dental hygiene programs.
Programs typically take 3 years to complete and offer laboratory, clinical, and classroom instruction. Areas of study include anatomy, medical ethics, and periodontics, which is the study of gum disease.
High school students interested in becoming dental hygienists should take courses in biology, chemistry, and math. Most dental hygiene programs also require applicants to complete prerequisites, which often include college-level courses. Specific requirements vary by school.
Licenses, Certifications, and Registrations
Every state requires dental hygienists to be licensed; requirements vary by state. In most states, a degree from an accredited dental hygiene program and passing written and clinical examinations are required for licensure. To maintain licensure, hygienists must complete continuing education requirements. For specific requirements, contact your state’s Board of Dental Examiners.
Many jobs also require cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) certification.
Contacts for More Information
For information about educational requirements and available accredited programs for dental hygienists, visit
American Dental Hygienists’ Association
For information about accredited programs and educational requirements, visit
Commission on Dental Accreditation, American Dental Association
The State Board of Dental Examiners in each state can provide information on licensing requirements.
Similar Occupations
This table shows a list of occupations with job duties that are similar to those of dental hygienists.
| Occupation | Job Duties | Entry-Level Education | Median Annual Pay, May 2022 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Dental Assistants |
Dental assistants provide patient care, take x rays, keep records, and schedule appointments. |
Postsecondary nondegree award | $44,820 |

|
Dentists |
Dentists diagnose and treat problems with patients’ teeth, gums, and related parts of the mouth. |
Doctoral or professional degree | $159,530 |

|
Medical Assistants |
Medical assistants complete administrative and clinical tasks, such as scheduling appointments and taking patients’ vital signs. |
Postsecondary nondegree award | $38,270 |

|
Physician Assistants |
Physician assistants examine, diagnose, and treat patients under the supervision of a physician. |
Master's degree | $126,010 |

|
Physicians and Surgeons |
Physicians and surgeons diagnose and treat injuries or illnesses and address health maintenance. |
Doctoral or professional degree | $229,300 |

|
Radiation Therapists |
Radiation therapists administer doses of radiation to patients who have cancer or other serious diseases. |
Associate's degree | $89,530 |
|
Radiologic and MRI Technologists |
Radiologic technologists perform diagnostic imaging examinations on patients. MRI technologists operate magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners to create diagnostic images. |
Associate's degree | $67,180 |

|
Registered Nurses |
Registered nurses (RNs) provide and coordinate patient care and educate patients and the public about various health conditions. |
Bachelor's degree | $81,220 |
